Ever wanted to build stunning, high-performance apps for iOS, Android, and the web from a single codebase? Meet Flutter. Created by Google, Flutter is an open-source UI toolkit that makes app development faster, simpler, and more expressive. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the absolute basics to get you started on your Flutter development journey.
Why Choose Flutter for App Development?
Flutter has rapidly gained popularity among developers worldwide, and for good reason. Here are the key advantages that make it a top choice for modern app development:
- Cross-Platform Power: Write your code once and deploy it on Android, iOS, Web, and Desktop. This saves an incredible amount of time and resources compared to native development.
- Rapid Development with Hot Reload: See your code changes reflected instantly without restarting your app. When I first ran
flutter create, I was amazed by how fast the hot reload works! This feature, known as Hot Reload, makes experimenting and debugging a breeze. - Expressive and Beautiful UIs: Flutter’s rich library of customizable widgets allows you to create pixel-perfect, branded designs that stand out in today’s competitive market.
- Native Performance: Your Flutter code compiles directly to native ARM machine code, ensuring your apps are fast and responsive, just like a native app.
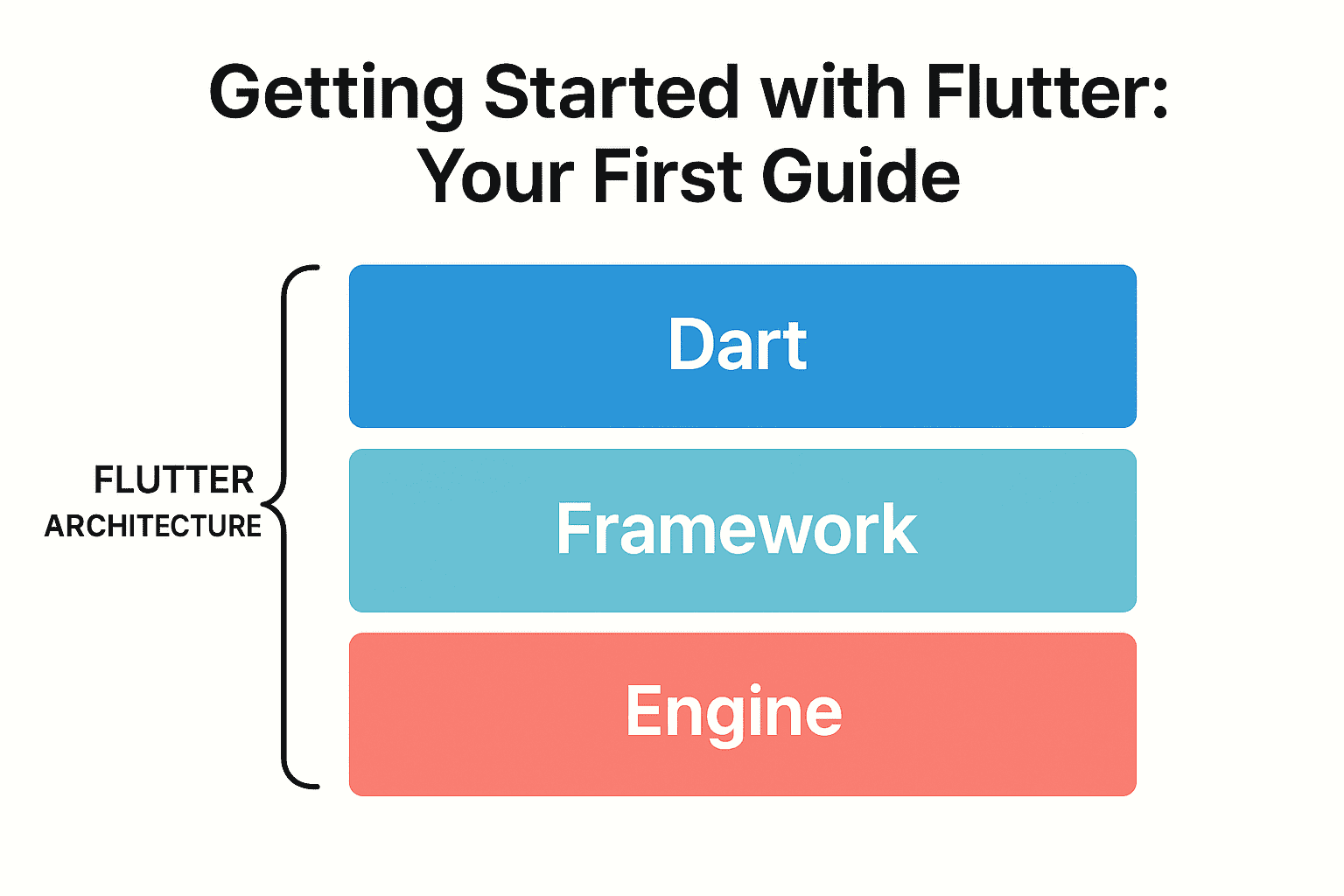
Understanding the Flutter Architecture
Before diving deeper into development, it’s helpful to understand what’s happening under the hood. Flutter’s architecture is built on three essential core layers:
- Dart Language: Flutter apps are written in Dart, a modern, client-optimized language developed by Google. It’s easy to learn and comes with powerful features like null safety.
- Flutter Framework: This is where the magic happens. It provides all the pre-built widgets (like buttons, text, and layouts), rendering libraries, and animation tools you’ll use to build your UI.
- Flutter Engine: Written primarily in C++, the engine is the low-level powerhouse that handles rendering, platform communication, and executing your Dart code.
Code Your First Flutter App: Hello, Flutter!
Now, let’s dive into some hands-on coding with a minimal “Hello, Flutter!” application:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(
const Center(
child: Text(
'Hello, world!',
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.blue),
),
),
);
}What’s Happening Here?
runApp(): This function inflates the given widget and attaches it to the screen, effectively starting your app.Center: A layout widget that centers its child widget on the screen.Text: A simple widget that displays a string of text.textDirection: We need to specify this here because we aren’t using theMaterialAppwidget, which normally handles this for us.
Tip: In almost all real-world applications, you’ll wrap your root widget with MaterialApp or CupertinoApp to get access to a ton of useful features, including navigation, theming, and Material Design components.
How to Set Up Your Flutter Environment
Ready to build this yourself? Setting up your development environment is straightforward, but let’s walk through each step carefully.
Step 1: Install the Flutter SDK
First, head over to the official Flutter installation guide to download the SDK for your operating system. Once downloaded, extract the ZIP file and add the flutter/bin directory to your system’s PATH variable. Additionally, you can find detailed setup instructions in the Flutter documentation.
Step 2: Install a Code Editor
Next, you’ll need an editor with Flutter and Dart support. The two most popular choices are:
- VS Code – Lightweight and highly customizable
- Android Studio – Full-featured with excellent debugging tools
Once installed, open your editor’s extension/plugin marketplace and install the official Flutter and Dart plugins. For more information about Dart programming basics, check out the official Dart language tour.
Step 3: Verify Your Installation
Finally, open your terminal or command prompt and run the following command:
flutter doctor
This powerful command checks your environment and shows a report of the status of your Flutter installation. If anything is missing, it will tell you exactly what to do next.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do I need textDirection?
The textDirection property is required when you’re not using Material or Cupertino app wrappers. It tells Flutter how to render text – left-to-right (LTR) for languages like English, or right-to-left (RTL) for languages like Arabic.
Can I run Flutter without VS Code?
Absolutely! While VS Code is popular, you can use any editor you prefer. Flutter works great with Android Studio, IntelliJ IDEA, or even command-line tools. The key is having the Flutter and Dart plugins installed.
Is Flutter really faster than native development?
Yes, Flutter’s development cycle is typically faster due to hot reload and single codebase deployment. However, for highly complex platform-specific features, you might still need some native code integration.
Your Next Steps in Learning Flutter
Congratulations! Your environment is now ready. From here, you can create and run your very first project:
- Create the project:
flutter create my_first_app - Run the project:
cd my_first_app flutter run
This will launch the default Flutter counter app on your connected device or emulator. Subsequently, you’re ready to move on to Part 2 – Setting Up Your First Flutter Project, where we’ll explore the project structure in detail.
Useful Resources
Keep experimenting with widgets and hot reload—it’s undoubtedly the best way to learn Flutter development! Moreover, don’t hesitate to explore the vast ecosystem of packages available on pub.dev to enhance your applications.
For more content Visit Deadloq. Thank You!!!