Flutter is a popular framework for building apps that run on Android, iOS, web, and desktop — all from a single codebase. If you’re starting with Flutter on Windows, here’s a complete guide to set up your development environment.
Follow the steps to setup Flutter in your Windows
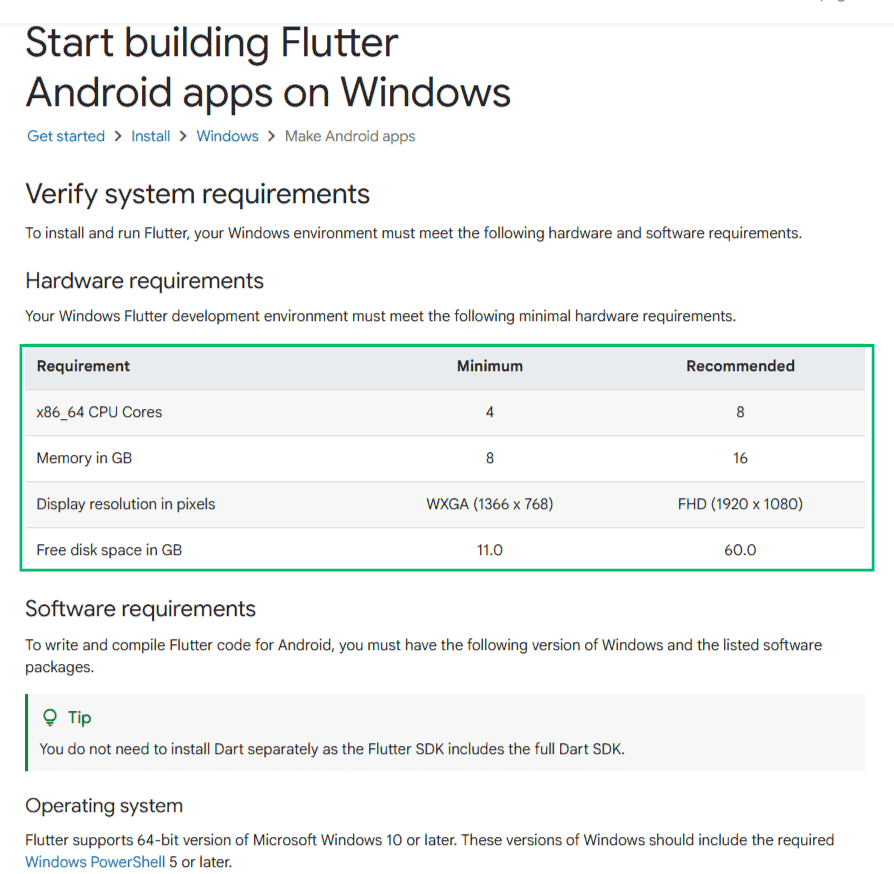
Step 1: Check Your System Requirements
Before installing Flutter, make sure your system meets these requirements:
- Operating System: Windows 10 or later (64-bit)
- Tools: PowerShell 5.0 or newer, Git for Windows (accessible from command line)
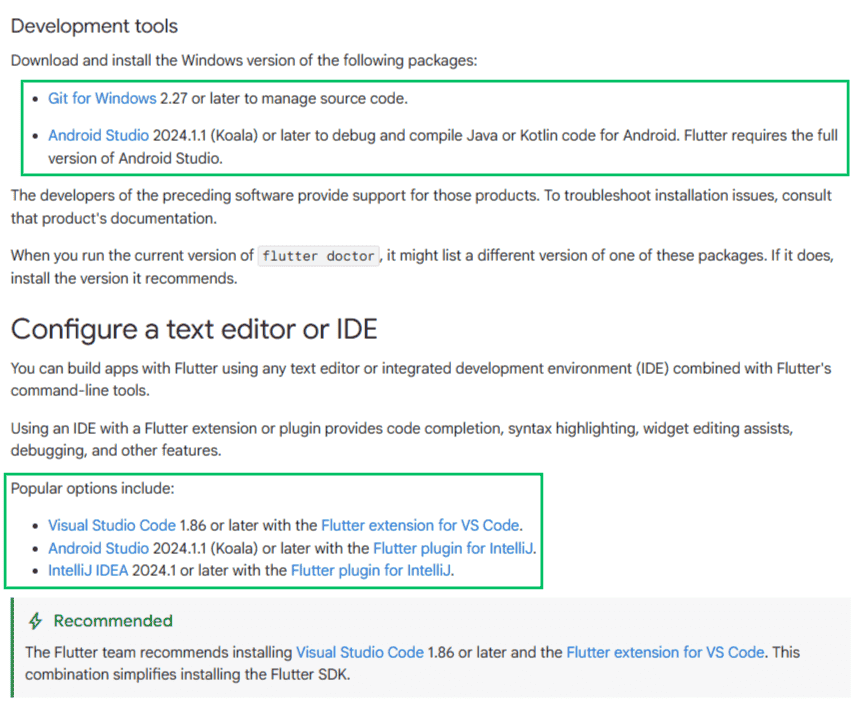
- Optional Development Tools: Visual Studio Code or Android Studio (recommended for building and testing apps)
Bonus step: Youtube video
Before we continue, you can also follow this short YouTube guide for visual instructions:
Step 2: Download Flutter SDK
- Visit the official Flutter website.
- Download the latest stable Flutter SDK ZIP file for Windows.
- Extract it to a folder with full read/write access, for example:
C:\Users\<YourUsername>\development\flutterAvoid system folders likeC:\Program Files.
Step 3: Restart the system after installing Git and Visual Studio Code on your windows.
Once you’re done with the installment of Git and VS Code, let’s get to the installation of Flutter Software development Kit (Flutter SDK). We have two ways to Install the Flutter SDK as shown in the image below. Select Download and install and Click on the “flutter_windows_version-stable.zip” file.
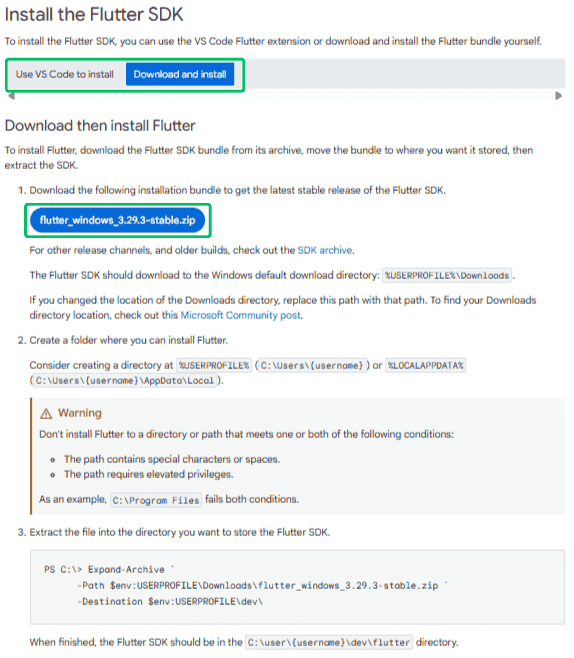
Flutter SDK is the essential tool that allows you to create Flutter projects, build them, and convert them into native mobile applications. In simpler terms, it is the core framework for developing Flutter UIs.
After downloading the ZIP file, extract the flutter folder (by drag-and-drop) to any location on your system where you have full read and write access. It’s recommended to create a dedicated folder outside the system drive to avoid permission issues. For example, you could use:
D:\development\flutter
Now double-click on the ‘flutter’ folder. Go to ‘flutter_console.bat’ file and double-click to open a command prompt window.
It should look like this :
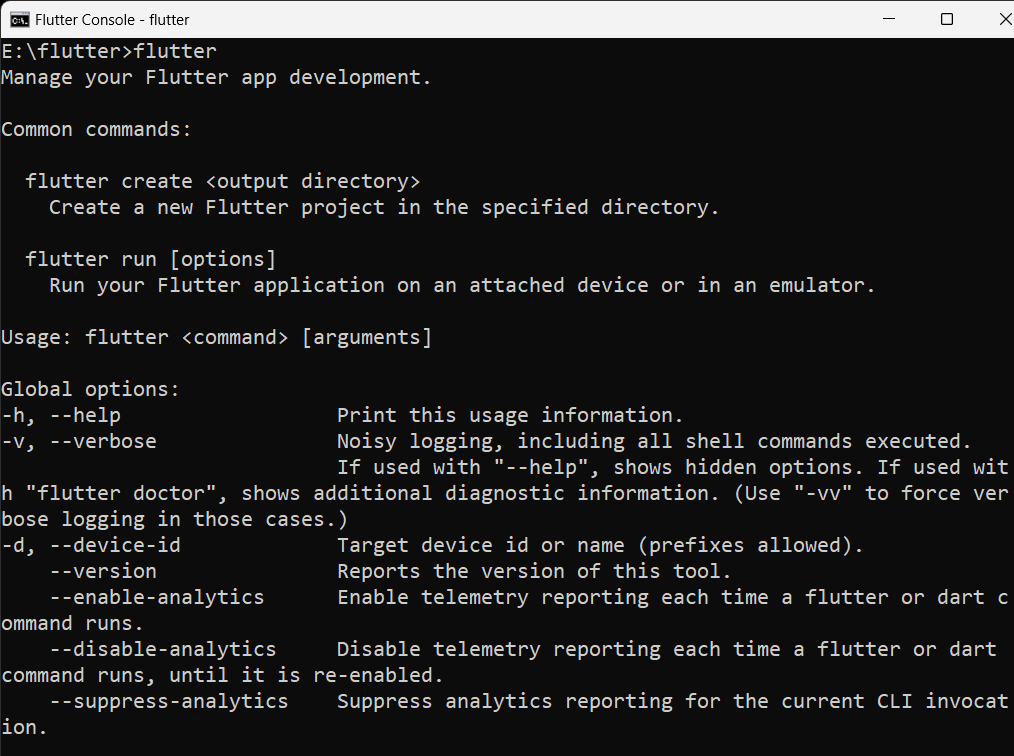
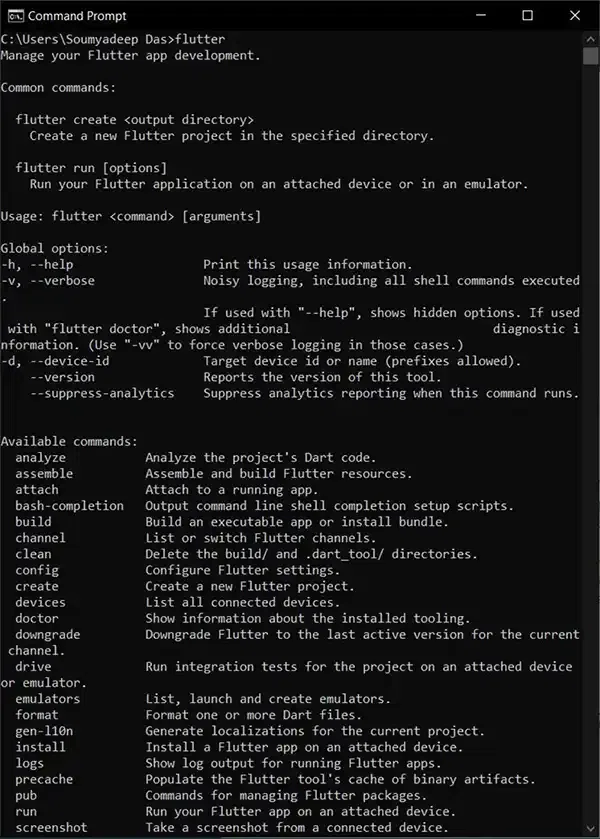
The console shown is actually a Windows terminal which is available for the developer to run flutter commands. Type in ‘flutter’ to get a list of all the flutter commands that can be run.
Something like this should pop :
Step 4: Check and edit environment variables for global system access.
To configure Flutter, you need to update your system PATH. On the official Flutter installation page, scroll down to the “Update your path” section for reference.
On Windows, follow these steps:
- Open Control Panel → System and Security → System → Advanced System Settings.
- Click Environment Variables….
- A dialog box will appear showing a list of your system’s environment variables.
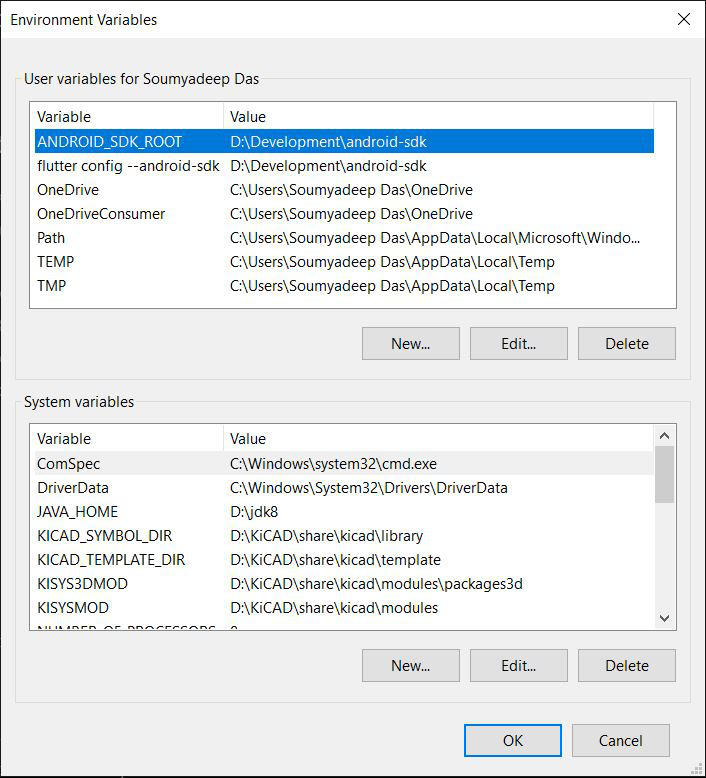
Environment Variables are global system settings that help manage various aspects of Windows. By adding the Flutter SDK to your environment variables, you can run Flutter commands directly from PowerShell or Command Promptwithout needing to execute the .bat file manually.
To do this, glance through the following steps:
- Check for ‘Path’ variable under User Variables list. If not already present, create a new variable (‘New…’) and assign the ‘flutter\bin‘ directory as its value.
- Now double-click on the ‘Path’ variable and add a new entry by double-clicking on a column below. It should look something like this:
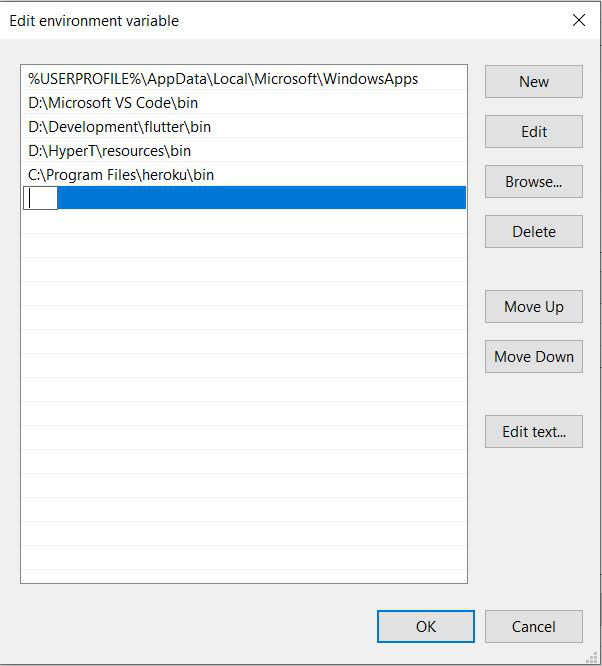
- In the path, copy the entire directory of flutter\bin folder and paste it. Click ‘Ok’ twice to complete the setup. Now, make sure that you have closed any existing Command Prompt/Windows PowerShell windows that are open.
Now, let’s verify whether Flutter is accessible globally.
- Open any terminal, such as Command Prompt or PowerShell.
- Type the following command:
flutter - If Flutter is set up correctly, you should see a list of Flutter commands, similar to what you would see when running the
.batfile.
If the commands appear as expected, congratulations — Flutter has been successfully configured system-wide!
If not, you may need to review the previous steps and ensure the PATH is correctly set.
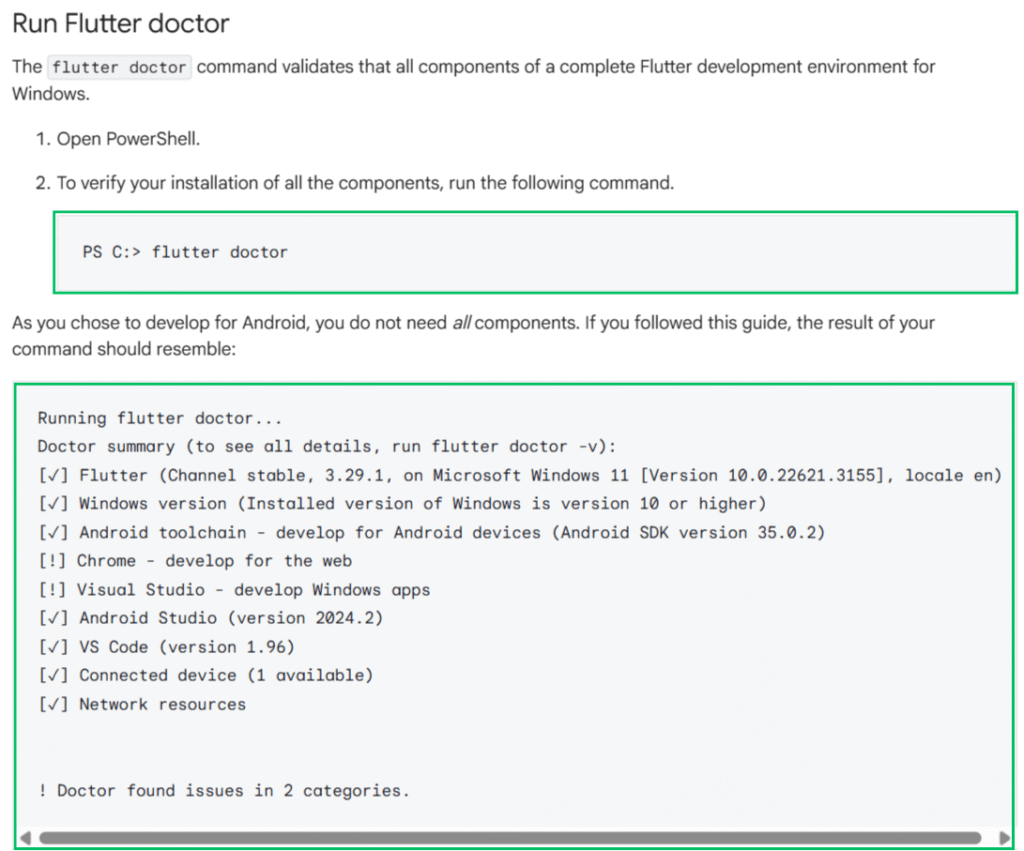
Step 5: Now, you have to analyze and check whether something is missing/has to be installed further.
To do this, under the Command Prompt terminal, type in ‘Flutter Doctor‘ to check for other requirements.
Step 6: Setting up Android tools and emulator for android devices.
The first step is to download and install Android Studio. To do this, navigate to the official page of Android Studio and click on ‘Download Android Studio‘.
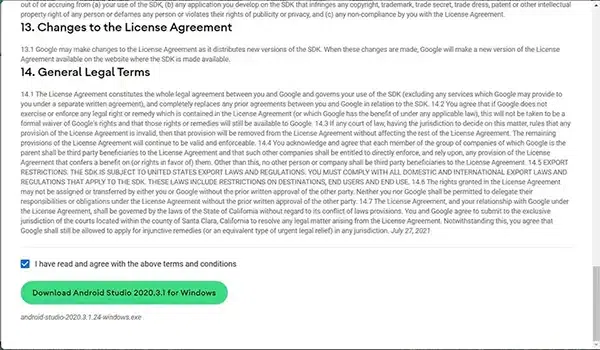
After accepting the license agreements, you are good to go! Click on the final Download button to start downloading.
After the download is complete, let’s move on to the next step, i.e. installation.
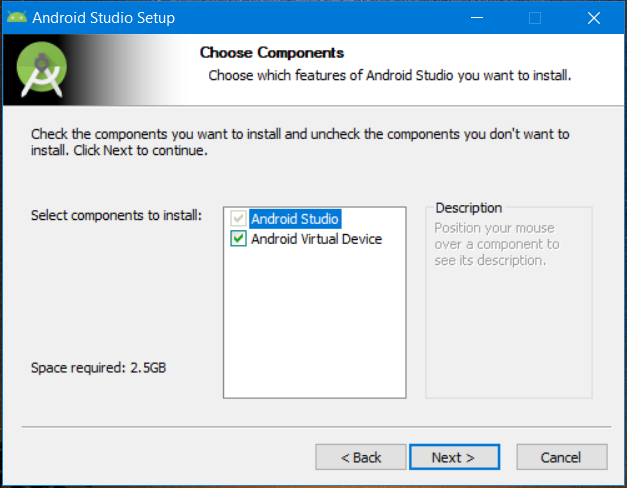
Under ‘Components‘, make sure that both Android Studio and Android Virtual Device are checked, and only then proceed. The Android Virtual Device is an essential tool for running various types and sizes of android emulators to test your flutter project. Henceforth, click on ‘Next‘.
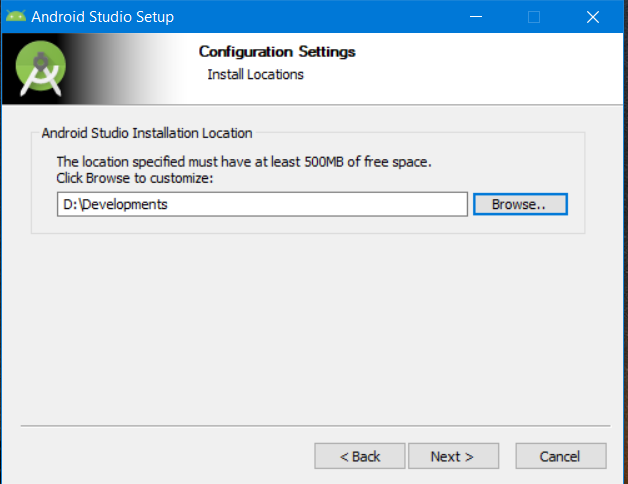
Select the directory you would want your file to be installed in. It is recommended to select some other path apart from the system drive. Once done, click on ‘Next‘.
Finally, click on ‘Install‘. Wait for a couple of seconds for the installation to complete. Check the box beside ‘Launch Android Studio‘. Click on ‘Finish‘.
Wait for Android Studio to launch on your computer. On the home screen, clickNext > Custom > Next.
For the Java Development kit location in the next step, it is recommended to keep the default path it requires, to avoid the hassle. In the next step, choose the UI appearance you’d like for Android Studio. Click ‘Next‘.
This next step is a bit important. Remember to check the required boxes exactly as shown below. If kits have already been installed, you can ignore those and move on. Click ‘Next‘. Set your desired folder for Android SDK.
With that done, click on ‘Finish‘. Android Studio will now install all the necessary android tools required for the execution of your flutter projects. This may take a significant time – it’s better to wait!
Now, we are ready to create and build flutter projects on Android Studio and run it on a real or a virtual Android device (emulator).
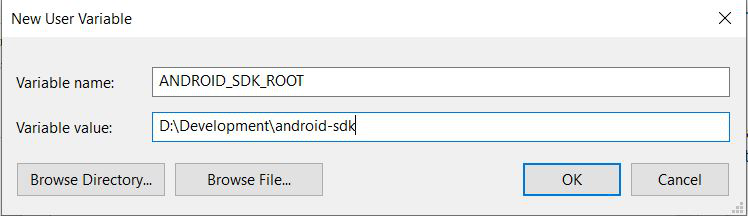
Step 7: Set SDK as an environment variable, for global access.
Now, open Command Prompt terminal and run ‘flutter doctor’ again. If you have installed Android SDK in the default directory suggested by Android Studio, there wouldn’t be any problem that would appear. Nevertheless, if you have installed it in a non-default directory, flutter would not be able to detect it in your system. To help it able to do that, you guessed it…we would be assigning it as an environment variable, giving global access.
As discussed earlier in Step 4, go to environment variables and click ‘New‘, and do the following (as recommended by flutter doctor). Click ‘OK‘.
Step 8: Accept required Android Licenses.
On the Command Prompt terminal, type in:
flutter doctor --android-licensesas suggested by flutter doctor. Hit Enter. To review licenses, type ‘y‘ for Yes.
You’ll see a couple of repeated prompts that look like this:
Accept? (y/N):Type ‘y‘ whenever asked for.
Finally, after all the license agreements have been accepted, you should see a message that looks something like this:
All SDK package licenses acceptedStep 9: Setup Android Emulator.
You have the option to choose between an Android Device or an Android Emulator to build your application on. It depends totally on you.
For setting up Android Device, go through the official docs page and follow the exact steps as mentioned. Download The Google USB Driver by following the link and install according to the instructions given. This can also be installed through Android Studio, which you can later connect to a real Android Device to build the application.
For setting up Android Emulator, you need to go through the following steps:
- Open Android Studio.
- On the topmost menu bar, click on Tools > SDK Manager.
- Verify whether you have the latest SDK installed. Remember to install the latest stable version too by checking on the box to the left.
In my case, it is ‘Android 9.0 (Pie)‘. You can even uncheck the latest version (if not stable), to not only save space but also run all your applications on the stable version itself. - Under the ‘SDK Tools‘ tab, don’t forget to check Google USB Driver to later connect a real Android Device. With that, click ‘Apply‘. Click ‘OK‘ to start SDK installation.
This might take a couple of minutes to complete. After the setup is done, click on ‘Finish‘. Your setup is now complete! - To have a first look at your Android Emulator, open Android Studio. Go to Tools > AVD Manager. A dialog box appears.
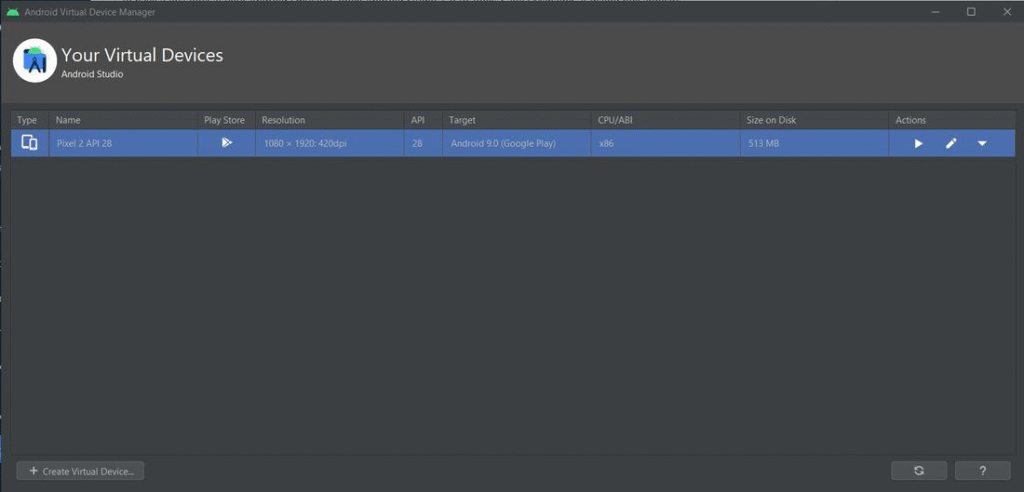
- Click on ‘Create Virtual Device…‘, select a device and its dimensions according to your preference, select a system image and lastly, under all default settings, click on ‘Finish’.
And that’s it! You now have a fully functional Flutter framework, complete with devices or emulators, ready for building beautiful apps. Dive in and start creating — the possibilities are endless!
Find More Content on Deadloq, Happy Learning!!